The State of Zero Trust Security in the Cloud Report by StrongDM

Contents
Built for Security. Loved by Devs.
- Free Trial — No Credit Card Needed
- Full Access to All Features
- Trusted by the Fortune 100, early startups, and everyone in between
As enterprises increasingly migrate workloads to the cloud, security strategies must adapt to meet evolving threats. Zero Trust, emphasizing identity verification and least privilege access, has become a critical framework for securing cloud environments. StrongDM’s recent survey of 600 cybersecurity professionals sheds light on the progress and challenges organizations face in adopting Zero Trust for the cloud.
Summary of Our Key Findings
Zero Trust Adoption Rates (go to this section)
- 81% of organizations have fully or partially implemented a Zero Trust model
- 19% are in the planning stage, with 0% reporting no plans to adopt Zero Trust
- 22% of respondents reported resistance from internal teams
- 48% pointed to cost and resource constraints
Cloud-Specific Priorities (go to this section)
- 84% of organizations are actively pursuing Zero Trust for cloud security
- 67% rank Identity and Access Management (IAM) and data encryption as top priorities
Tooling and Implementation (go to this section)
- 52% of teams use a mix of tools, while only 30% rely on unified solutions
- 28% use the same tools across cloud and on-premises environments, highlighting challenges in achieving a unified approach
Database Security (go to this section)
- 89% of teams apply or are developing Zero Trust for database security, yet only 43% have robust measures in place
Challenges and Gaps (go to this section)
- 49% cite managing policies across multi-cloud environments as a top challenge
- 57% report minimal to no strict controls for database and data access
Critical Features for Zero Trust Solutions (go to this section)
- 60% prioritize real-time monitoring and anomaly detection
- 45% seek simplified policy management across multi-cloud environments
Zero Trust Adoption Rates
81% of organizations have fully or partially implemented a Zero Trust model
This high adoption rate is encouraging as it reflects a broad recognition of Zero Trust as an essential component of modern cybersecurity strategies. It indicates that organizations are urgently prioritizing the implementation of identity-verified and least privilege access controls to address evolving security challenges in increasingly complex environments.
19% are in the planning stage, with 0% reporting no plans to adopt Zero Trust
This underscores its necessity in modern cybersecurity, as organizations universally recognize its critical role in mitigating risks and ensuring robust defenses against evolving threats. Additionally, 22% of respondents reported resistance from internal teams, reflecting the challenges in aligning stakeholders on the need for and benefits of Zero Trust adoption. 48% pointed to cost and resource constraints, emphasizing the financial and operational investment needed to implement Zero Trust at scale.
Cloud-Specific Priorities
84% of organizations are actively pursuing Zero Trust for cloud security
This data underscores the growing momentum behind Zero Trust as a critical framework for cloud security. Organizations are recognizing that as cloud adoption expands, so do the risks—and that Zero Trust offers a robust solution to address these challenges by continuously verifying users and limiting access to only what is necessary.
67% rank Identity and Access Management (IAM) and data encryption as top priorities
IAM is critical because it forms the foundation of Zero Trust by ensuring that only verified identities can access sensitive resources. Data encryption complements this by securing information at rest and in transit, making it inaccessible to unauthorized users. Together, these elements reinforce the core principles of Zero Trust: continuous verification and least privilege access.
Tooling and Implementation
52% of teams use a mix of tools, while only 30% rely on unified solutions
Relying on a mix of tools can lead to challenges in enforcement and consistency, as fragmented systems often result in gaps or overlaps in security coverage. Unified solutions, on the other hand, provide streamlined management, reducing complexity and ensuring consistent application of Zero Trust principles across environments.
28% use the same tools across cloud and on-premises environments, highlighting challenges in achieving a unified approach
This disparity implies potential inefficiencies, such as duplicate efforts in policy management and increased complexity in maintaining consistent security standards. Moreover, relying on separate tools can introduce risks like misconfigurations or gaps in visibility, which could be exploited by malicious actors.
Database Security
89% of teams apply or are developing Zero Trust for database security, yet only 43% have robust measures in place
Zero Trust is critical for database systems because these systems often house the most sensitive and valuable data in an organization, such as customer information, financial records, and intellectual property. Without Zero Trust, databases are vulnerable to unauthorized access, insider threats, and data breaches. Implementing Zero Trust principles, such as least privilege access, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring, ensures that only authorized users can access the data they need, when they need it, significantly reducing the risk of breaches and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Challenges and Gaps
49% cite managing policies across multi-cloud environments as a top challenge
This difficulty arises because each cloud platform often has its own unique tools, interfaces, and security requirements, making it hard to maintain consistency. These discrepancies can lead to misconfigurations, gaps in security coverage, and added complexity for IT teams. As a result, the effectiveness of Zero Trust strategies may be compromised, highlighting the need for tools that simplify policy management and provide unified oversight across diverse environments.
57% report minimal to no strict controls for database and data access
This is particularly worrisome given the sensitive nature of databases, which often store critical information like customer data, intellectual property, and financial records. A lack of strict controls increases the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance failures, underscoring the need for robust Zero Trust measures to protect these high-value targets.
Critical Features for Zero Trust Solutions
60% prioritize real-time monitoring and anomaly detection
Real-time monitoring is a critical feature for Zero Trust as it enables organizations to detect and respond to threats as they occur, rather than after the damage is done. By continuously auditing access and flagging anomalies, it helps organizations proactively manage risks, ensure compliance, and maintain trust in their security posture.
45% seek simplified policy management across multi-cloud environments
Managing policies in multi-cloud environments is challenging due to the unique tools, interfaces, and security protocols of each cloud provider. This fragmentation can result in inconsistent policy enforcement, misconfigurations, and increased security gaps, leaving organizations vulnerable to breaches. Simplifying policy management reduces these risks by ensuring uniform application of Zero Trust principles, streamlining operations, and enabling IT teams to focus on proactive security measures rather than troubleshooting discrepancies.
Breakdown of the Findings
Top Outcomes Organizations Prioritize in Their Zero Trust Strategies

In the StrongDM survey, we asked organizations to rate the importance of various outcomes for their Zero Trust strategies, revealing the most critical priorities for modern security approaches:
Improved Data Security and Protection
69% rated this as “Very Important.”
Data security is the backbone of Zero Trust, ensuring sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access.
Reduced Risks of Unauthorized Access
67% rated it as “Very Important.”
This outcome highlights Zero Trust’s core principle of minimizing security vulnerabilities by continuously verifying identities and access requests.
Enhanced Threat Detection and Response
62% rated this as “Very Important.”
The ability to detect and respond to threats swiftly is crucial in today’s evolving threat landscape.
Enhanced Control Over Access
50% rated this as “Very Important.”
Controlling who accesses what resources is a key pillar of Zero Trust frameworks.
Stronger Regulatory and Compliance Alignment
41% rated it as “Very Important,” while another 46% found it “Important.”
As compliance requirements grow, organizations see alignment with regulatory standards as a significant benefit of Zero Trust.
Operational Efficiency
43% rated it as “Very Important.”
Balancing security and efficiency remains a priority as teams work to implement Zero Trust without slowing down operations.
Increased Visibility into Access and Activities
40% rated it as “Very Important,” with another 40% finding it “Important.”
Organizations value the insight Zero Trust provides into user behaviors and resource interactions.

Understanding how cybersecurity professionals prioritize their intended outcomes underlines how Zero Trust not only enhances security but also aligns with broader organizational goals like compliance, operational efficiency, and proactive threat management.
Top Challenges in Implementing Zero Trust Strategies in Multi-Cloud Environments
 Organizations face several obstacles when adopting Zero Trust strategies across multi-cloud environments. The key challenges include:
Organizations face several obstacles when adopting Zero Trust strategies across multi-cloud environments. The key challenges include:
1. The Complexity of Managing Policies Across Different Clouds
49% of respondents cited this as a major challenge, highlighting the difficulty of maintaining consistent security policies across diverse cloud platforms.
2. Cost and Resource Requirements
48% pointed to cost and resource constraints, emphasizing the financial and operational investment needed to implement Zero Trust at scale.
3. Difficulty in Achieving Visibility Across All Environments
34% reported visibility challenges, which can hinder the ability to detect and respond to threats effectively in a multi-cloud setup.
4. Insufficient Tooling or Platform Support
30% noted a lack of adequate tools or support, indicating the need for more robust and compatible solutions tailored for Zero Trust in multi-cloud architectures.
5. Lack of Understanding of Zero Trust Principles
23% cited knowledge gaps as a barrier, underscoring the importance of education and training to drive adoption.
6. Resistance from Internal Teams
22% faced internal pushback, reflecting challenges in aligning stakeholders on the need for and benefits of Zero Trust.
7. Integration with Legacy Systems
21% struggled with legacy system integration, as outdated infrastructure often complicates Zero Trust implementation.
This data highlights the complexities of implementing Zero Trust in multi-cloud environments, with cost, policy management, and visibility emerging as the most pressing challenges. Addressing these issues requires a combination of education, advanced tooling, and strategic planning to ensure successful adoption.
Top Zero Trust Priorities for Cloud Security: IAM and Data Encryption Lead the Way
 As organizations adopt Zero Trust principles for cloud security, some aspects are seen as more critical than others. The 600 cybersecurity professionals in our survey were asked to rate the importance of various Zero Trust components for their cloud strategies, revealing clear priorities:
As organizations adopt Zero Trust principles for cloud security, some aspects are seen as more critical than others. The 600 cybersecurity professionals in our survey were asked to rate the importance of various Zero Trust components for their cloud strategies, revealing clear priorities:
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
62% rated IAM as “Very Important.”
As the cornerstone of Zero Trust, IAM's role in verifying and limiting access makes it a top priority for most organizations.
2. Data Security and Encryption
67% of respondents rated it “Very Important,” the highest among all categories.
Protecting sensitive data through encryption is a non-negotiable for modern cloud security.
3. Endpoint Security and Device Trust Verification
64% of respondents rated it “Very Important.”
Ensuring device security reinforces Zero Trust by verifying trustworthiness at every endpoint.
4. Secure Remote Access
60% rated it “Very Important.”
Remote work trends have pushed secure access to the forefront of Zero Trust strategies.
5. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
58% ranked it as “Very Important.”
MFA adds an essential layer of security by requiring multiple identity verifications.
Other components like Continuous Monitoring and Logging (46%) and Privileged Access Management (42%) also received significant attention, reflecting their critical roles in maintaining robust Zero Trust environments.
Micro-Segmentation (19%) and Contextual Access Control (30%), while vital, were rated lower, possibly due to their complexity or current implementation challenges.
This data highlights how organizations prioritize Zero Trust elements to address their immediate cloud security needs while recognizing the importance of building a comprehensive strategy.
52% of Teams Use a Mix of Tools for Enforcing Zero Trust in the Cloud
 As organizations strive to implement Zero Trust principles in cloud environments, their approach to tooling reveals varying levels of maturity:
As organizations strive to implement Zero Trust principles in cloud environments, their approach to tooling reveals varying levels of maturity:
- 52% of teams rely on a mix of tools for specific Zero Trust functions, though they lack a unified solution. This fragmented approach highlights the challenge many organizations face in achieving seamless Zero Trust implementation.
- 30% have adopted an integrated, comprehensive Zero Trust toolset, positioning them as leaders in Zero Trust maturity.
- 16% are actively evaluating tools to support Zero Trust but have yet to implement any solutions.
- Only 1.5% are not considering Zero Trust tools for cloud security, which underscores the model's widespread relevance.
This data highlights the increasing dedication to Zero Trust strategies, despite the challenges teams face with disjointed solutions. Embracing unified, all-in-one tools is essential for organizations aiming to unlock the full potential of Zero Trust and strengthen their cloud security posture.
61% of Teams Use Different Approachs for Zero Trust Across Cloud and On-Premises
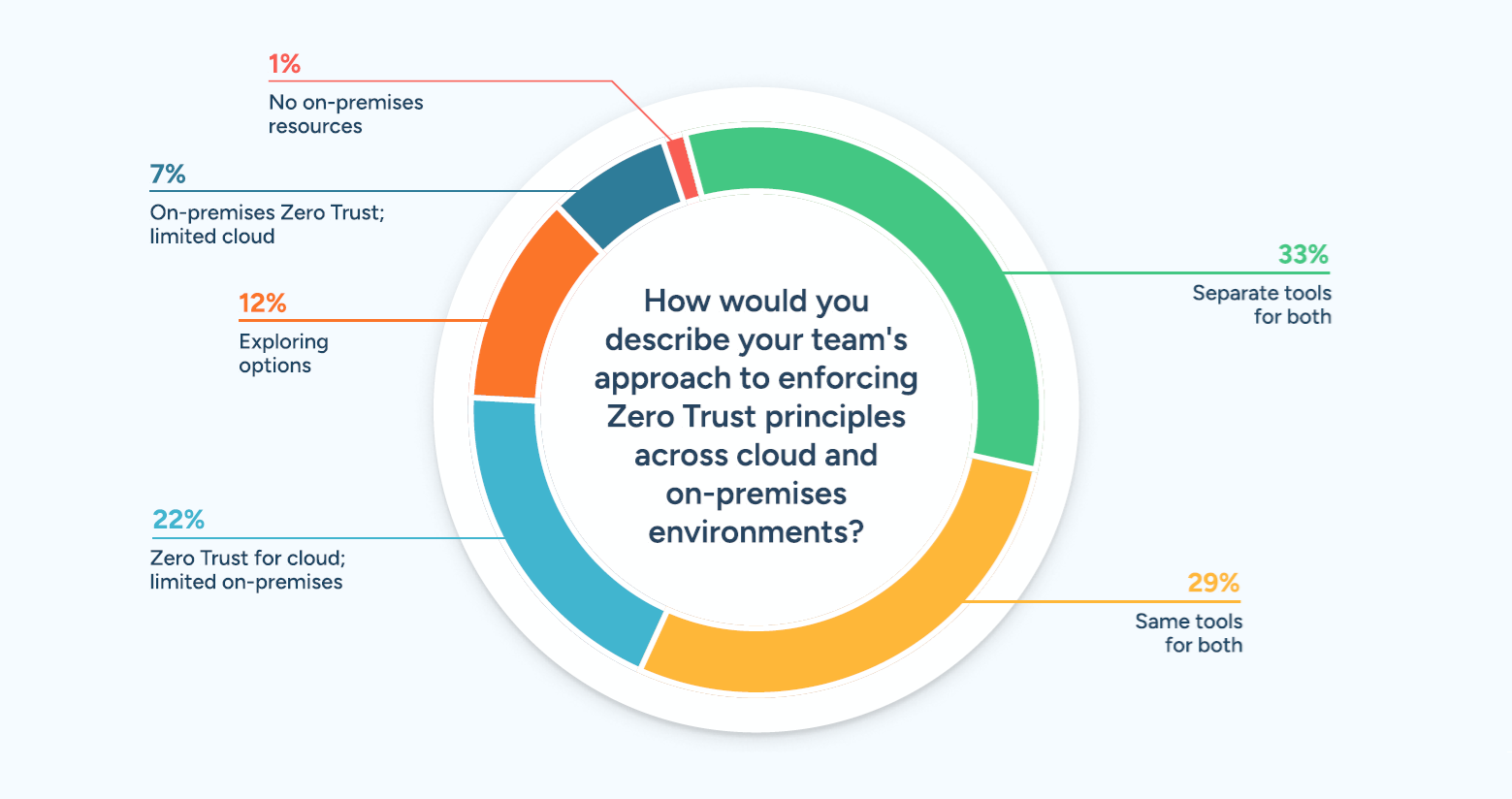 The approach organizations take to enforce Zero Trust principles across their cloud and on-premises environments varies significantly, reflecting their infrastructure and security priorities:
The approach organizations take to enforce Zero Trust principles across their cloud and on-premises environments varies significantly, reflecting their infrastructure and security priorities:
- 29% use the same tools for Zero Trust across both cloud and on-premises environments, showcasing a unified approach to managing security.
- 33% employ separate tools for Zero Trust in cloud and on-premises settings, indicating a more segmented strategy based on the unique requirements of each environment.
- 22% focus primarily on Zero Trust for cloud environments, with limited coverage for on-premises systems, reflecting the shift toward cloud-first strategies.
- 7% primarily focus on on-premises Zero Trust, with limited cloud coverage, suggesting legacy infrastructure still plays a significant role for some teams.
- 12% are exploring options for a unified Zero Trust approach across both environments, signaling an interest in simplifying and consolidating security tools.
- Only 1% of respondents reported not having any on-premises resources, highlighting the enduring presence of hybrid environments.
As the evidence indicates, enterprise security teams employ diverse strategies to enforce Zero Trust, with many organizations working toward more integrated and comprehensive solutions to protect both cloud and on-premises assets.
89% of Teams Use or Are Developing Zero Trust for Database Security
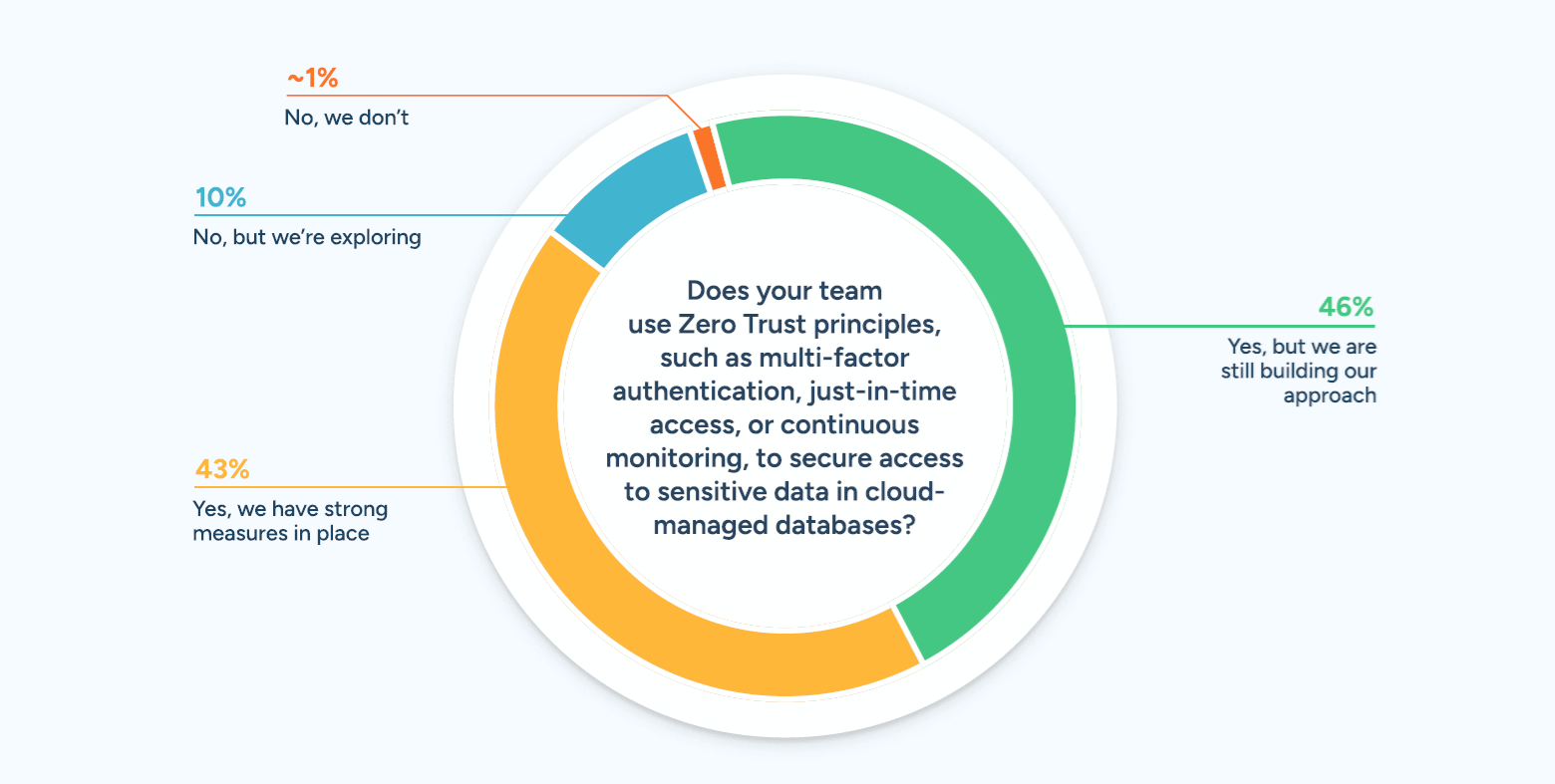 Zero Trust principles are becoming a cornerstone for securing sensitive data in cloud-managed databases. Our survey highlights the state of adoption:
Zero Trust principles are becoming a cornerstone for securing sensitive data in cloud-managed databases. Our survey highlights the state of adoption:
- 43% of teams have strong Zero Trust measures in place for database security, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), just-in-time (JIT) access, and continuous monitoring.
- 46% are building out their approach, actively working to implement Zero Trust principles for enhanced database protection.
- 10% are exploring options for implementing Zero Trust, reflecting growing awareness of its importance for securing sensitive cloud-managed data.
- Less than 1% reported not having any Zero Trust measures specifically for databases, emphasizing its near-universal recognition as a critical security priority.
The data makes it clear that there is widespread adoption of Zero Trust for database security, with most organizations either having robust measures in place or actively working toward implementation. As database threats evolve, Zero Trust principles like MFA, JIT access, and continuous monitoring are becoming essential tools for safeguarding sensitive data.
74% of Teams Secure Cloud CLI Access with MFA and Strict Controls

Securing access to cloud provider command-line interfaces (CLI) is a critical aspect of Zero Trust strategies. Our survey reveals how teams are addressing this:
- 74% of respondents use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strict access controls to secure CLI access, highlighting these as the most common and effective measures.
- 56% log and monitor CLI activities in real time, ensuring visibility into user actions and enabling rapid detection of suspicious behavior.
- 38% restrict CLI access based on roles, reflecting the importance of role-based access control (RBAC) in limiting privileges to only what is necessary.
- 4% reported not applying Zero Trust principles to CLI access, showing there is still a small gap in security adoption for this critical interface.
This data highlights a strong trend toward securing CLI access using multiple layers of Zero Trust measures, such as MFA, real-time monitoring, and role-based restrictions. As CLI access remains a potential vulnerability, these practices are essential for reducing risks and ensuring secure interactions with cloud provider environments.
RBAC and ABAC Lead the Way in Enforcing Least Privilege Across Cloud Accounts
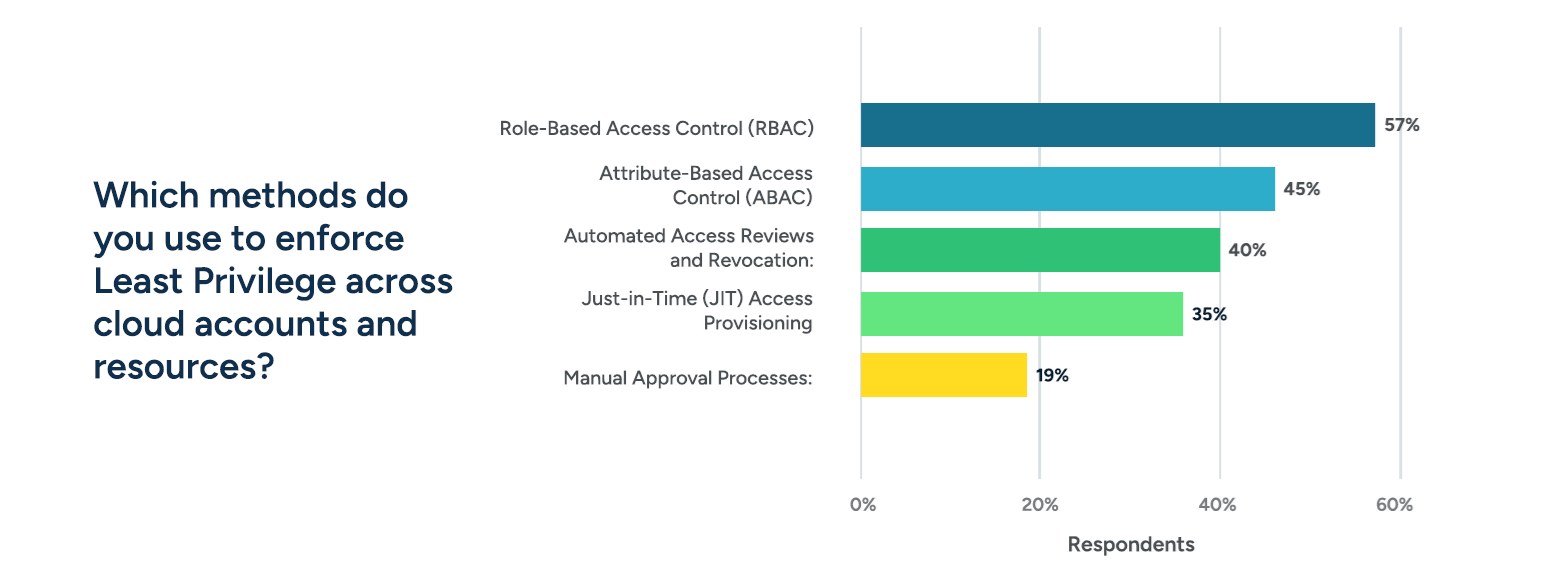
To enforce the principle of Least Privilege across cloud accounts and resources, organizations are adopting various methods, with some approaches standing out as the most widely used:
1. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
57% of respondents use RBAC, making it the most popular method. By assigning permissions based on user roles, RBAC ensures that individuals only have access to what they need.
2. Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
45% reported using ABAC, which allows more granular control by basing access decisions on user attributes, such as location or device type.
3. Automated Access Reviews and Revocation
40% utilize automated processes to review and revoke unnecessary access, ensuring privileges remain current and relevant.
4. Just-in-Time (JIT) Access Provisioning
35% employ JIT provisioning, granting temporary access as needed and revoking it once tasks are complete, minimizing exposure.
5. Manual Approval Processes
19% still rely on manual approvals for access requests, reflecting a less automated approach to enforcing Least Privilege.
This data highlights a strong emphasis on automation and dynamic control mechanisms like RBAC, ABAC, and JIT provisioning. While manual processes remain in use, the trend toward automated access reviews and attribute-driven policies underscores the industry’s focus on efficiency and precision in access management.
61% of Teams Use Real-Time Monitoring to Audit Cloud Access Grants

Auditing access grants to cloud resources is a crucial component of maintaining security and enforcing Zero Trust principles. Check out how survey respondents approach this challenge:
Real-Time Monitoring of Access Changes: 61% of teams rely on real-time monitoring to track access changes, ensuring immediate visibility and responsiveness to potential issues.
Regular Automated Access Reviews: 54% use automated reviews to routinely audit and validate access grants, leveraging efficiency and minimizing manual effort.
Manual Periodic Access Audits: 46% conduct manual audits periodically, adding an additional layer of scrutiny to their access management processes.
Third-Party Access Management Tools: 37% leverage third-party tools, reflecting the growing role of specialized solutions in simplifying and enhancing access audits.
6% do not currently audit access grants, indicating an area for improvement in securing cloud resources.
1% reported using other methods, demonstrating unique or customized approaches tailored to specific needs.
The survey responses highlight how crucial it is to combine automation with real-time functionality for effectively auditing access grants. While manual processes and third-party tools play important roles, the trend toward automated and dynamic solutions reflects the industry's focus on scalability and precision in cloud security.
60% of Teams Use Centralized Secrets Management for Cloud Resources

Managing credentials, keys, and secrets securely is a critical part of cloud resource management. Our survey highlights how teams handle this responsibility:
1. Centralized Secrets Management Systems
60% of respondents use centralized systems like AWS Secrets Manager, making it the most popular method for securing sensitive credentials and automating management tasks.
2. Cloud-Native Key Management Services (KMS)
50% leverage cloud-native KMS, such as those provided by AWS, Azure, or GCP, to manage encryption keys and secrets securely.
3. In-House or Custom-Built Secrets Storage
43% use custom-built solutions, reflecting the need for tailored approaches in some organizations despite the availability of commercial tools.
4. Manual Management and Rotation
22% manually manage credentials, highlighting a less automated and more error-prone approach still used by some teams.
5. Other Methods
2% reported using other approaches, including unique or hybrid solutions.
This data shows a strong trend toward centralized and automated solutions, with cloud-native and third-party systems dominating the landscape. However, the continued reliance on manual processes by some organizations underscores an area for improvement, especially as the complexity of cloud environments grows.
IAM and MFA Tools Lead the Way in Zero Trust Strategies
 Organizations are leveraging a variety of tools to implement Zero Trust strategies, with some solutions standing out as the most widely used:
Organizations are leveraging a variety of tools to implement Zero Trust strategies, with some solutions standing out as the most widely used:
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM) Tools
64% of respondents reported using IAM tools, making them the cornerstone of most Zero Trust strategies. These tools ensure secure, role-based access to critical systems and data.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Tools
58% utilize MFA tools, adding an essential layer of verification to secure access points.
3. VPNs
57% still rely on VPNs, highlighting their continued relevance as part of a layered Zero Trust approach.
4. Privileged Access Management (PAM) Tools
44% use PAM solutions to secure and manage privileged accounts, reducing risks from insider threats and credential misuse.
5. Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
41% reported using CASB tools, reflecting their growing role in protecting cloud environments by monitoring and enforcing policies.
6. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
33% employ EDR solutions, enhancing threat detection and response capabilities for endpoint devices.
7. Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) Solutions
34% utilize ZTNA solutions, underscoring their importance in replacing traditional network perimeter defenses with identity- and context-based access controls.
8. Secrets Management Tools
25% leverage these tools for securely managing credentials, keys, and sensitive information.
9. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions
33% use DLP tools, emphasizing the importance of safeguarding sensitive data and preventing leaks.
Other Tools
- Continuous monitoring and logging solutions (26%), Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools (34%), and device trust management solutions (21%) are also widely used.
- 4% do not currently use specific tools for Zero Trust, revealing room for growth in adoption.
This data reflects a strong trend toward using comprehensive and integrated toolsets, such as IAM, MFA, and PAM, as the foundation of Zero Trust strategies. While some organizations continue to rely on traditional solutions like VPNs, the adoption of advanced tools like ZTNA and CASB indicates a shift toward more modern and dynamic security practices.
The Path Forward: Zero Trust as a Security Imperative
The data is clear: Zero Trust is rapidly becoming the standard for securing cloud and on-premises environments. While challenges remain, the growing adoption and prioritization of Zero Trust principles signal a promising future for organizations aiming to enhance their cybersecurity posture.
Methodology
StrongDM surveyed 600 US-based cybersecurity workers in November 2024. The survey was completed online via Pollfish, and responses were random, voluntary, and completely anonymous.
About StrongDM
StrongDM simplifies Zero Trust implementation with unified, identity-first access solutions that secure both cloud and on-premises resources. From seamless IAM integration to real-time monitoring and granular access controls, StrongDM ensures that businesses can build resilient defenses without added complexity.
Next Steps
StrongDM unifies access management across databases, servers, clusters, and more—for IT, security, and DevOps teams.
- Learn how StrongDM works
- Book a personalized demo
- Start your free StrongDM trial

Categories:

About the Author
Michaline Todd, Marketing Expert, is a distinguished marketing leader with a track record spanning over two decades in the software industry. With tenure of over 10 years as a Chief Marketing Officer, she has left an indelible mark on companies such as Oracle, Veritas, MarkLogic, Evident.io, Palo Alto Networks, and StrongDM. Michaline's expertise lies at the intersection of technology and marketing, driving strategic initiatives that fuel business growth and innovation.
You May Also Like