Add a Google Kubernetes Engine Cluster
Last modified on April 7, 2025
This guide describes how to manage access to an Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster. Adding a GKE cluster takes place in the StrongDM Admin UI, Google Cloud Console, and Google Developers Console.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure that the GKE endpoint you are connecting is accessible from one of your StrongDM gateways or relays. See our guide on nodes for more information.
If you are using kubectl 1.30 or higher, it will default to using websockets, which the StrongDM client did not support prior to version 45.35.0. This can be remedied by taking one of the following actions:
- Update your client to version 45.35.0 or greater.
- Set the environment variable
KUBECTL_REMOTE_COMMAND_WEBSOCKETS=falseto restore the previous behavior in your kubectl.
Add Your GKE Cluster in the StrongDM Admin UI
Log in to the Admin UI and go to Infrastructure > Clusters.
Click the Add cluster button.
Select Google Kubernetes Engine as the Server Type and set other resource properties to configure how the StrongDM relay connects.
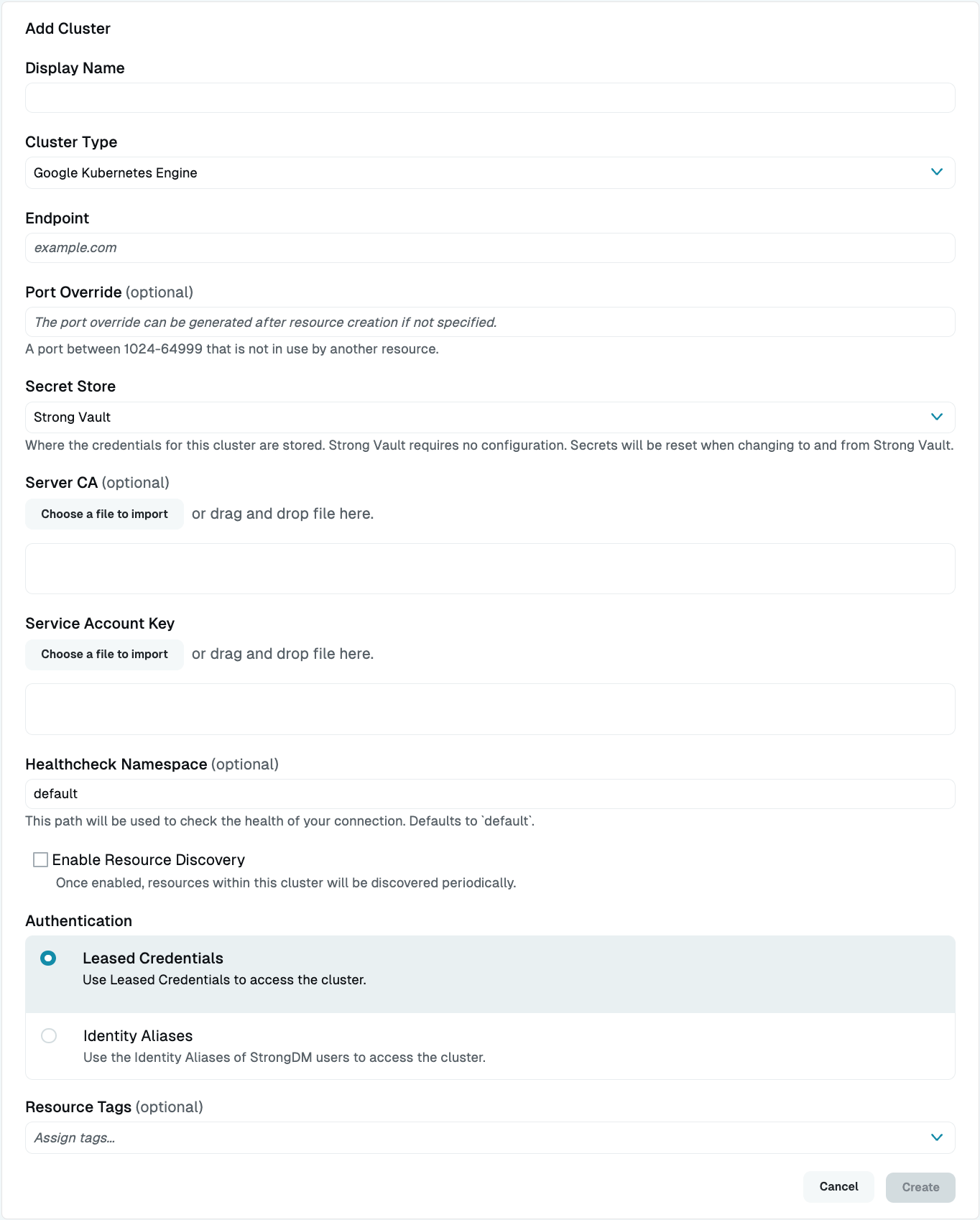
Google Kubernetes Engine Cluster Setup in Admin UI Click Create to save the resource.
The Admin UI updates and shows your new cluster in a green or yellow state. Green indicates a successful connection. If it is yellow, click the pencil icon to the right of the server to reopen the Connection Details screen. Then click Diagnostics to determine where the connection is failing.
Resource properties
Configuration properties are visible when you add a Cluster Type or when you click to view the cluster’s settings. The following table describes the settings available for your GKE cluster.
| Property | Requirement | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Display Name | Required | Meaningful name to display the resource throughout StrongDM; exclude special characters like quotes (") or angle brackets (< or >) |
| Cluster Type | Required | Select Google Kubernetes Engine |
| Proxy Cluster | Required | Defaults to “None (use gateways)”; if using proxy clusters, select the appropriate cluster to proxy traffic to this resource |
| Endpoint | Required | Endpoint of the GKE cluster, such as 35.232.191.126; relay server should be able to connect to your GKE endpoint |
| IP Address | Optional | Shows up when a loopback range is configured for the organization; local IP address used to connect to this resource using the local loopback adapter in the user’s operating system; defaults to 127.0.0.1 |
| Port Override | Read only | Automatically generated with a value between 1024 to 59999 as long as that port is not used by another resource; preferred port can be modified later under Settings > Port Overrides; after specifying the port override number, you must also update the kubectl configuration, which you can learn more about in section Port Overrides |
| Secret Store | Optional | Credential store location; defaults to Strong Vault; to learn more, see Secret Store options |
| Server CA | Required | Server CA, which is available under the Show Credentials link just to the right of the endpoint in the Google Cloud Platform console |
| Service Account Key | Required | Service account key in JSON format; you can generate this key in the Google Developers Console; ensure it is associated with a user having the appropriate level of access to the cluster for your use case; once generated, upload the key using the button below the Service Account Key box |
| Healthcheck Namespace | Optional | If enabled for your organization, the namespace used for the resource healthcheck; defaults to default if empty; supplied credentials must have the rights to perform one of the following kubectl commands in the specified namespace: get pods, get deployments, or describe namespace |
| Enable Resource Discovery | Optional | Enables automatic discovery within this cluster |
| Authentication | Required | Authentication method to access the cluster; select either Leased Credential (default) or Identity Aliases (to use the Identity Aliases of StrongDM users to access the cluster) |
| Identity Set | Required | Displays if Authentication is set to Identity Aliases; select an Identity Set name from the list |
| Healthcheck Username | Required | If Authentication is set to Identity Aliases, the username that should be used to verify StrongDM’s connection to it; username must already exist on the target cluster |
| Resource Tags | Optional | Resource tags consisting of key-value pairs <KEY>=<VALUE> (for example, env=dev) |
Display name
Some Kubernetes management interfaces, such as Visual Studio Code, do not function properly with cluster names containing spaces. If you run into problems, please choose a Display Name without spaces.
Google credentials
When your users connect to this cluster, they have exactly the rights permitted by this Google Service Account key. See this Google document for more information.
Secret Store options
By default, server credentials are stored in StrongDM. However, these credentials can also be saved in a secrets management tool.
Non-StrongDM options appear in the Secret Store dropdown menu if they are created under Settings > Secrets Management. When you select another Secret Store type, its unique properties display. For more details, see Configure Secret Store Integrations.