Latest blog posts from John

Discover how StrongDM's Zero Trust PAM and fine-grained authorization secure cloud data plane access and mitigate shadow access risks without hindering productivity.

Learn why Just-in-Time (JIT) access is essential for Zero Trust security in AWS environments. Discover how StrongDM's JIT access enhances security, optimizes workflows, and ensures compliance with Zero Trust principles.
Zero Trust cloud security is a cybersecurity model that operates on the principle that no user, device, system, or action should be trusted by default — even if it's inside your organization’s own network. This approach minimizes the risk of breaches and other cyber threats by limiting access to sensitive information and resources based on user roles, device security posture, and contextual factors.
If organizations hope to minimize their exposure to attacks and mitigate any damage done by a threat, they must have a comprehensive incident response plan. An effective plan will detect, contain, and enable rapid recovery from security breaches, preserving your business continuity and operability. We've outlined seven incident response steps for you to follow so you can be prepared for a threat.
The HIPAA Omnibus Rule strengthens privacy and security protections for patient health information, extends liability to business associates, and increases penalties for non-compliance.

Kubernetes (K8S) has revolutionized software development, but managing such a complex system with numerous components can be challenging. Fortunately, there are several best practices your team can adopt to secure your K8S environment and reduce your attack surface. By implementing these Kubernetes ...

Privileged Identity Management (PIM) is a complex cybersecurity approach. But it’s the only proven method you can use to lock down access and protect your precious resources. It can help you keep cybercriminals out and ensure that even your trusted users can’t accidentally—or intentionally—jeopardize your system’s security.
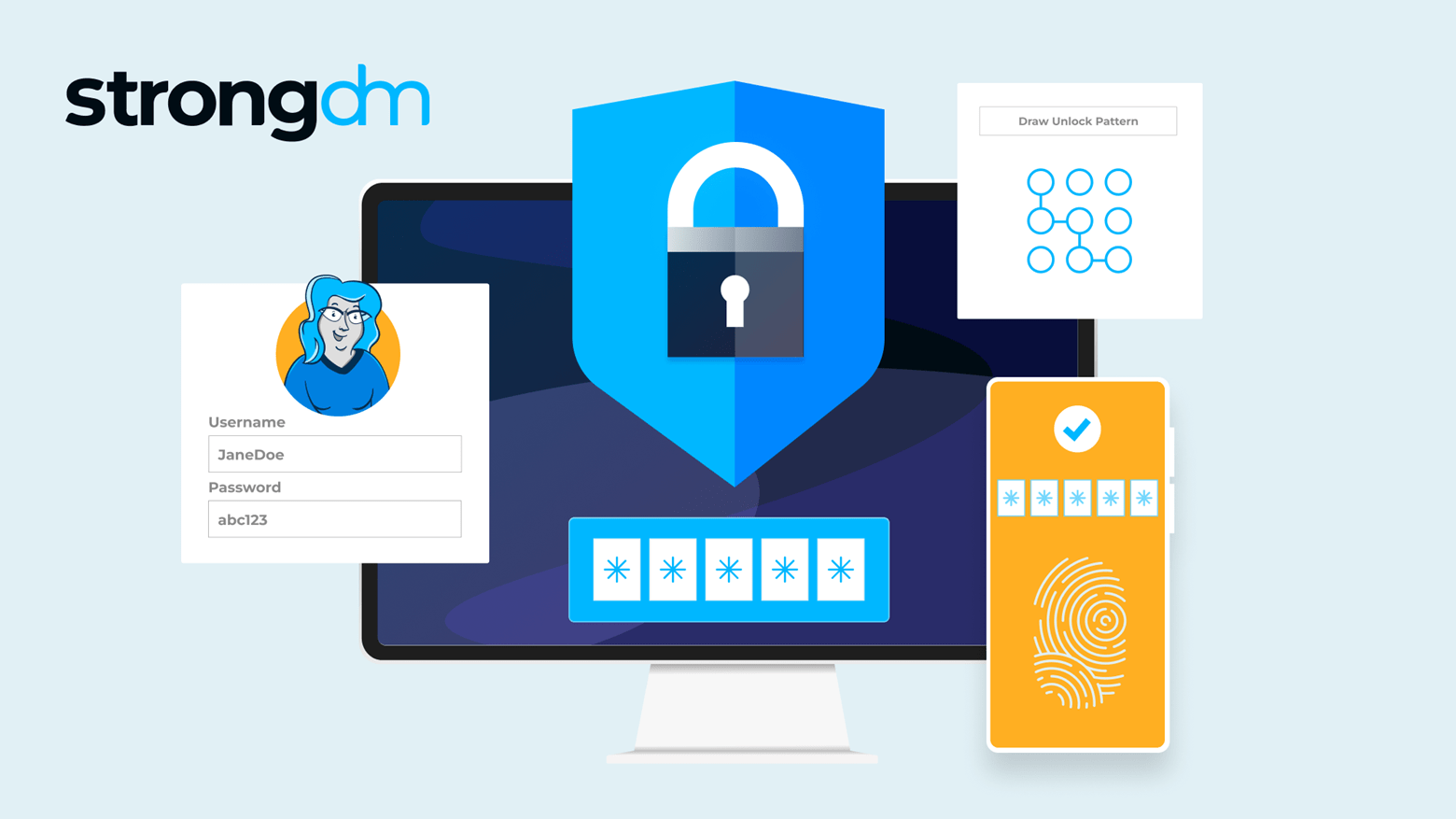
With so many advanced cyber attackers lurking on the threat landscape, a simple password is no longer enough to safeguard your sensitive data. There are many reasons to adopt MFA for your business. It supplements your security by requiring additional information from users upon their access requests—and it significantly reduces your risk of incurring a breach. Several multi-factor authentication methods are available, with varying strengths and weaknesses. Be sure to compare the differences

SQL injection attacks remain one of the most prevalent and dangerous threats to database security. These attacks can compromise sensitive data, disrupt operations, and cause significant financial and reputational damage. Understanding how to prevent SQL injection attacks will help you foster a security-conscious organizational culture.

Internet of Things (IoT) devices form the backbone of many modern businesses, facilitating operations, collecting valuable data, and enhancing efficiency. However, the widespread deployment of these devices creates numerous entry points for potential attackers. Without robust security measures, you risk exposing critical systems and sensitive information to malicious actors.
Traditional security measures like simple virus protection, firewalls, and web and email filtering are no longer sufficient to safeguard against the sophisticated tactics used by modern cybercriminals. This heightened complexity means you must implement advanced defense mechanisms that go beyond basic protections, ensuring a resilient and adaptive cybersecurity posture.
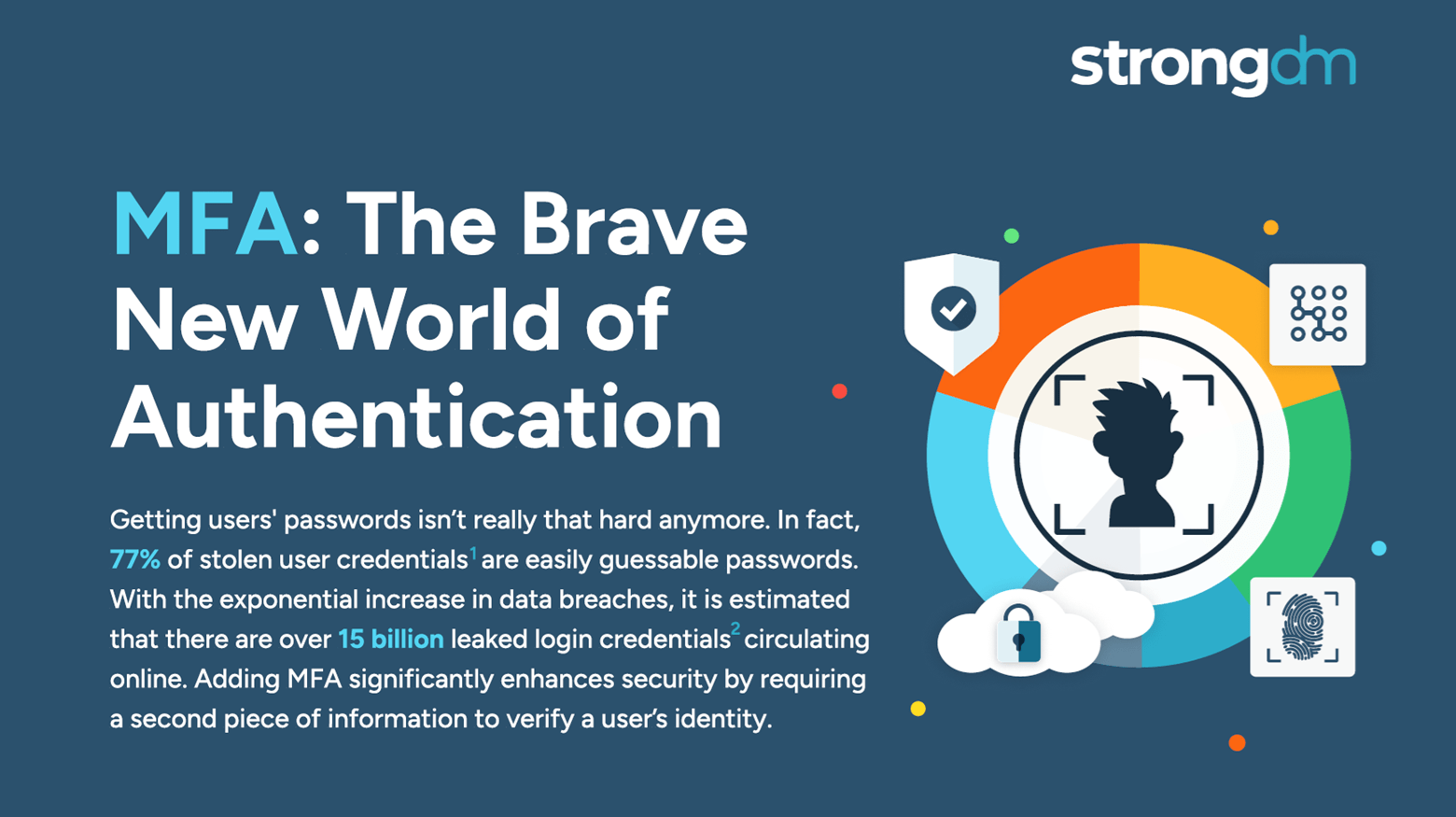
Get ready to secure everything and anything with MFA. Easily combine security checks such as device trust and geo-location. With StrongDM you can MFA all resources (e.g., multiple clouds, diverse databases, or critical applications, etc.) without changing your applications’ code or infrastructure.

This article investigates MFA fatigue attacks. We'll explain how they work, why they're effective, and who they typically target. We'll also provide real-life examples to help your team detect and prevent these threats. You'll leave with a clear understanding of MFA fatigue attacks and tips on how to shore up your cloud security to defend against them.