
Written by
John MartinezLast updated on:
September 6, 2024Reading time:
Contents
Built for Security. Loved by Devs.
- Free Trial — No Credit Card Needed
- Full Access to All Features
- Trusted by the Fortune 100, early startups, and everyone in between
The CIS Kubernetes Benchmark is a set of prescriptive recommendations assembled to guide administrators to achieve good security hygiene and results in strengthened security outcomes for their Kubernetes environments.
Because the recommendations are prescriptive (as they are for most of the CIS Benchmarks), they describe a specific command or setting to be made on a Kubernetes component, what problem the recommendation mitigates, the test for a successful outcome and a remediation to satisfy the recommendation.
At the end of the recommendation made by the CIS Benchmark, there is a mapping to specific CIS Critical Security Controls Safeguards. The Controls Safeguards are aligned with StrongDM’s capabilities.
CIS Recommendations Guidelines for StrongDM
Our role in helping Kubernetes admins focuses on proactive prevention. Meaning, of the relevant recommendations, StrongDM would prevent the issue described from happening in the first place.
StrongDM proactively prevents the following issues addressed by CIS for Kubernetes: the Kubernetes API service (Section 1.2), Authentication and Authorization System (Section 3.1), and the RBAC and Service Accounts Components (Section 5.1).
1. Standing access and standing privileges
StrongDM’s Access Workflows and Just-In-Time access capabilities allow teams to implement access to critical Kubernetes administrative components only when needed and for the duration required. Eliminate standing access and privileges to Kubernetes admins and grant access to components only when needed via automated and manual workflows.
2. Credentials exposure
StrongDM never exposes the credentials needed to access target resources, including Kubernetes, to end users. Rather, the credentials are obtained from a secure vault of your choosing, and exchanged between the StrongDM Gateway and Resource in an encrypted exchange and are never stored on permanent media.
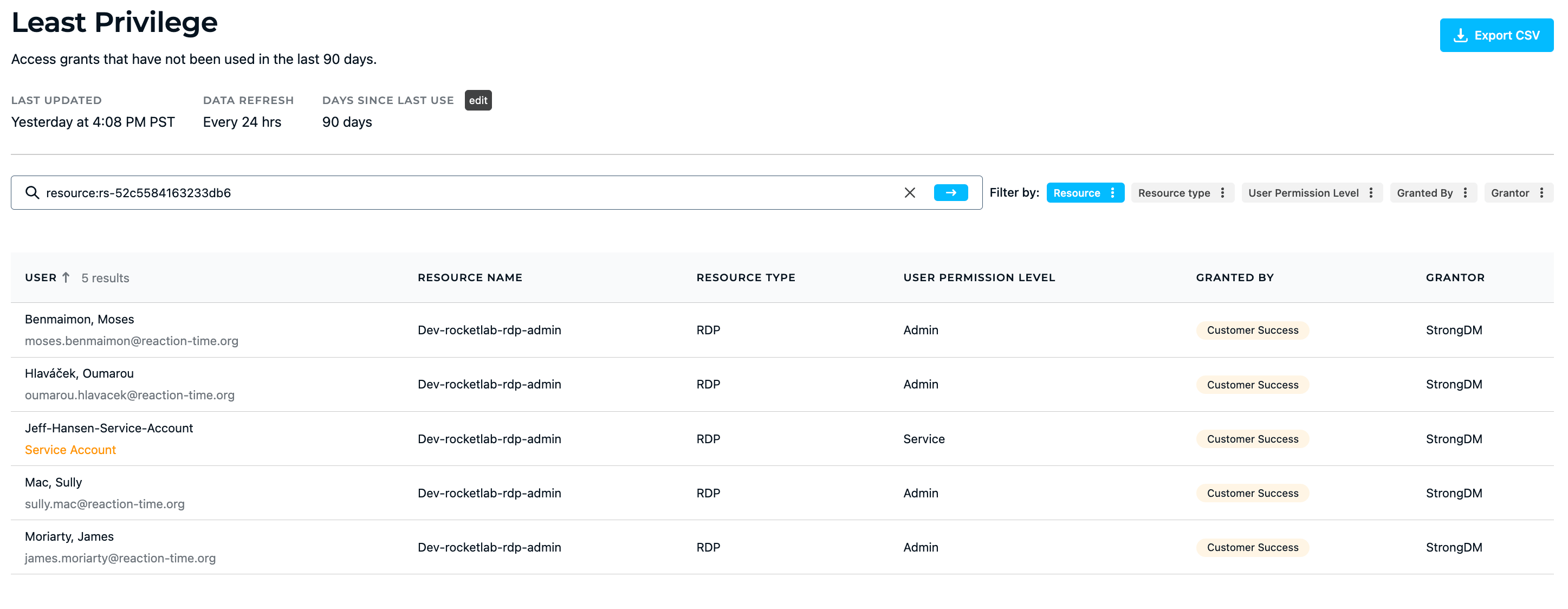
3. Least privilege reporting
The StrongDM Least Privilege Report provides information about access grants to Kubernetes and other resources that have been inactive for a certain period of time, displaying information such as the user’s name and permission level, the name and type of resource they were granted access, and the last time the resource was accessed. This report allows admins to easily see which users are not using the resources available to them, and assess whether or not their access should be revoked.
💡Make it easy: Fine-tune least privilege by analyzing and responding to comprehensive access insights. Easily report on which privileges are being used (or not). Try it for yourself.
4. Session recording and audit logs for auditing and visibility
StrongDM provides session recordings and audit logs for all access to Kubernetes resources, including the kubectl commands issued, which are critical for identifying root cause and responsible entity in security incidents. This improves Mean Time to Investigate (MTTI) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) to any incident.
Conclusion: StrongDM Is Critical for Implementing CIS Kubernetes Benchmark
StrongDM provides a robust set of capabilities that simplify access, while maintaining the most secure posture for administrative access to Kubernetes. Support of Kubernetes is just one component that makes up our Zero Trust PAM platform. Knowing that Kubernetes hosts and is adjacent to a myriad of applications and services critical to your business, we also support resources such as databases and cloud accounts, legacy as well as cloud-native applications, and we centralize access to every one of those resources.
Want to see more Zero Trust PAM Kubernetes in action? Book a demo.
Next Steps
StrongDM unifies access management across databases, servers, clusters, and more—for IT, security, and DevOps teams.
- Learn how StrongDM works
- Book a personalized demo
- Start your free StrongDM trial

Categories:

About the Author
John Martinez, Technical Evangelist, has had a long 30+ year career in systems engineering and architecture, but has spent the last 13+ years working on the Cloud, and specifically, Cloud Security. He's currently the Technical Evangelist at StrongDM, taking the message of Zero Trust Privileged Access Management (PAM) to the world. As a practitioner, he architected and created cloud automation, DevOps, and security and compliance solutions at Netflix and Adobe. He worked closely with customers at Evident.io, where he was telling the world about how cloud security should be done at conferences, meetups and customer sessions. Before coming to StrongDM, he lead an innovations and solutions team at Palo Alto Networks, working across many of the company's security products.
You May Also Like