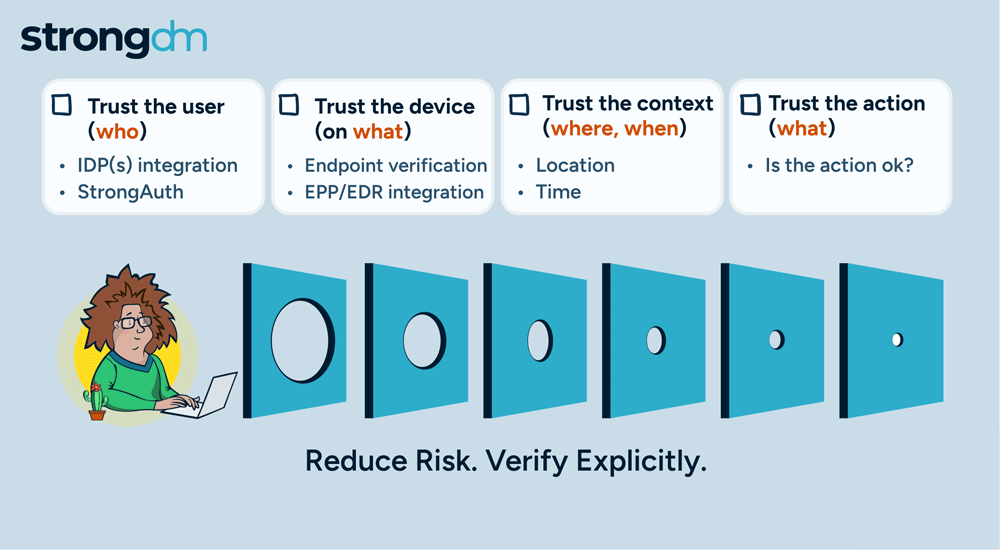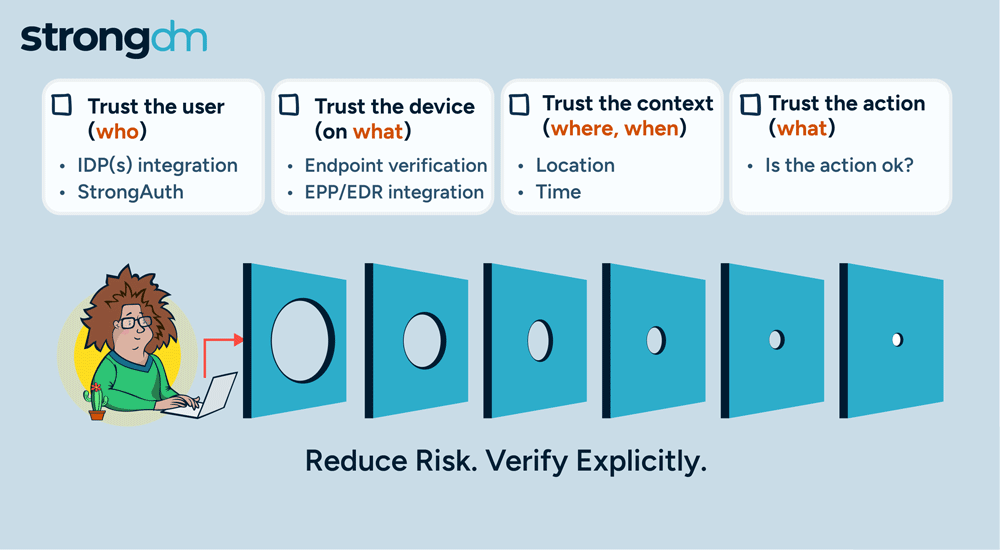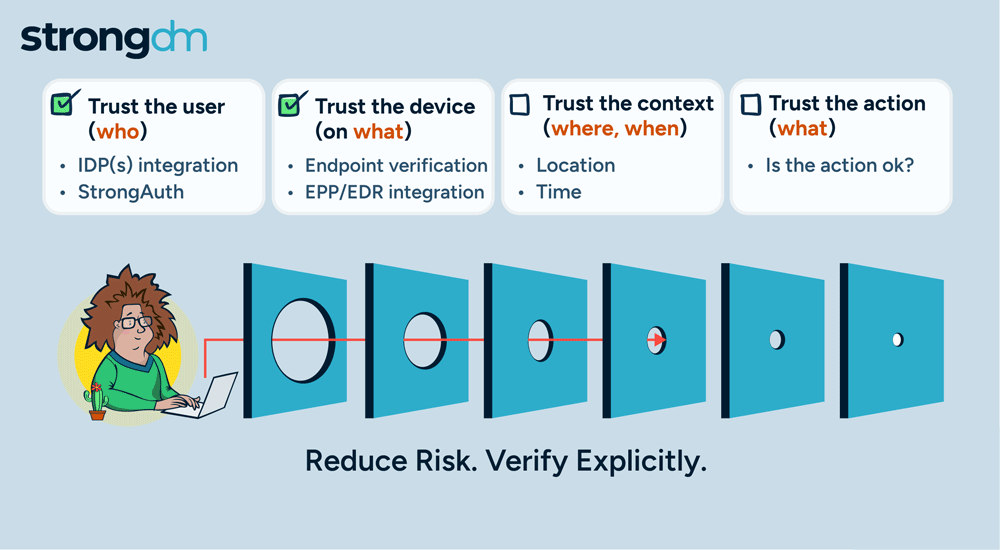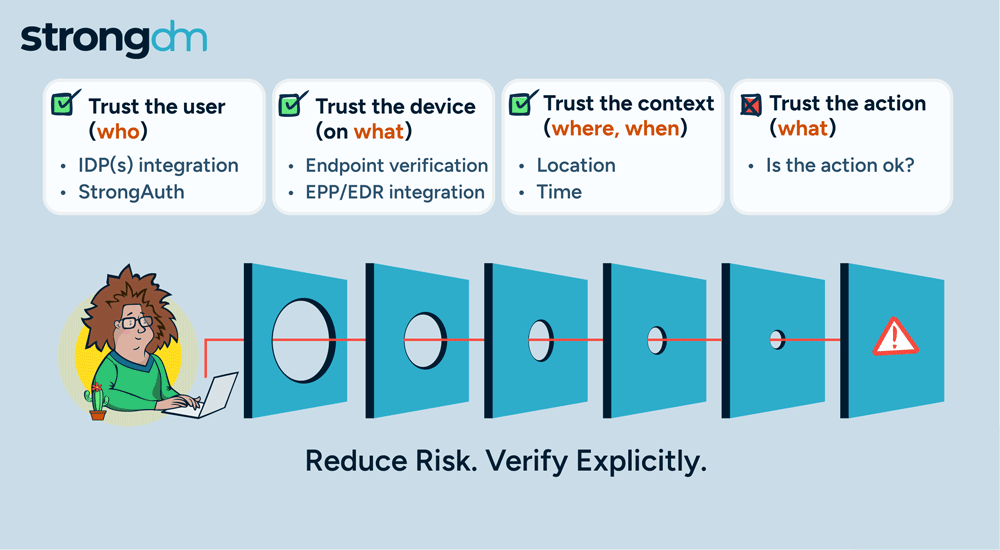
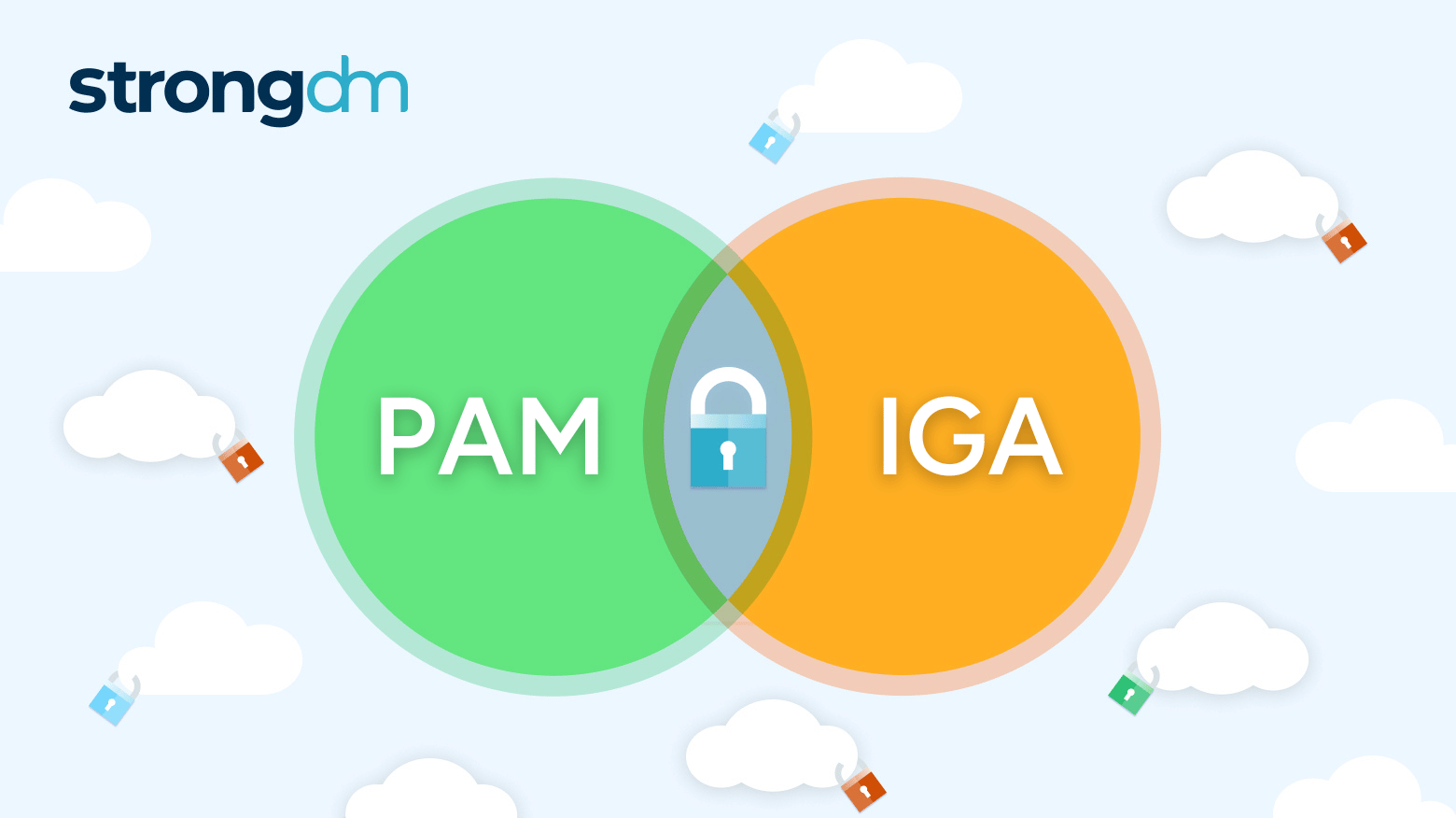
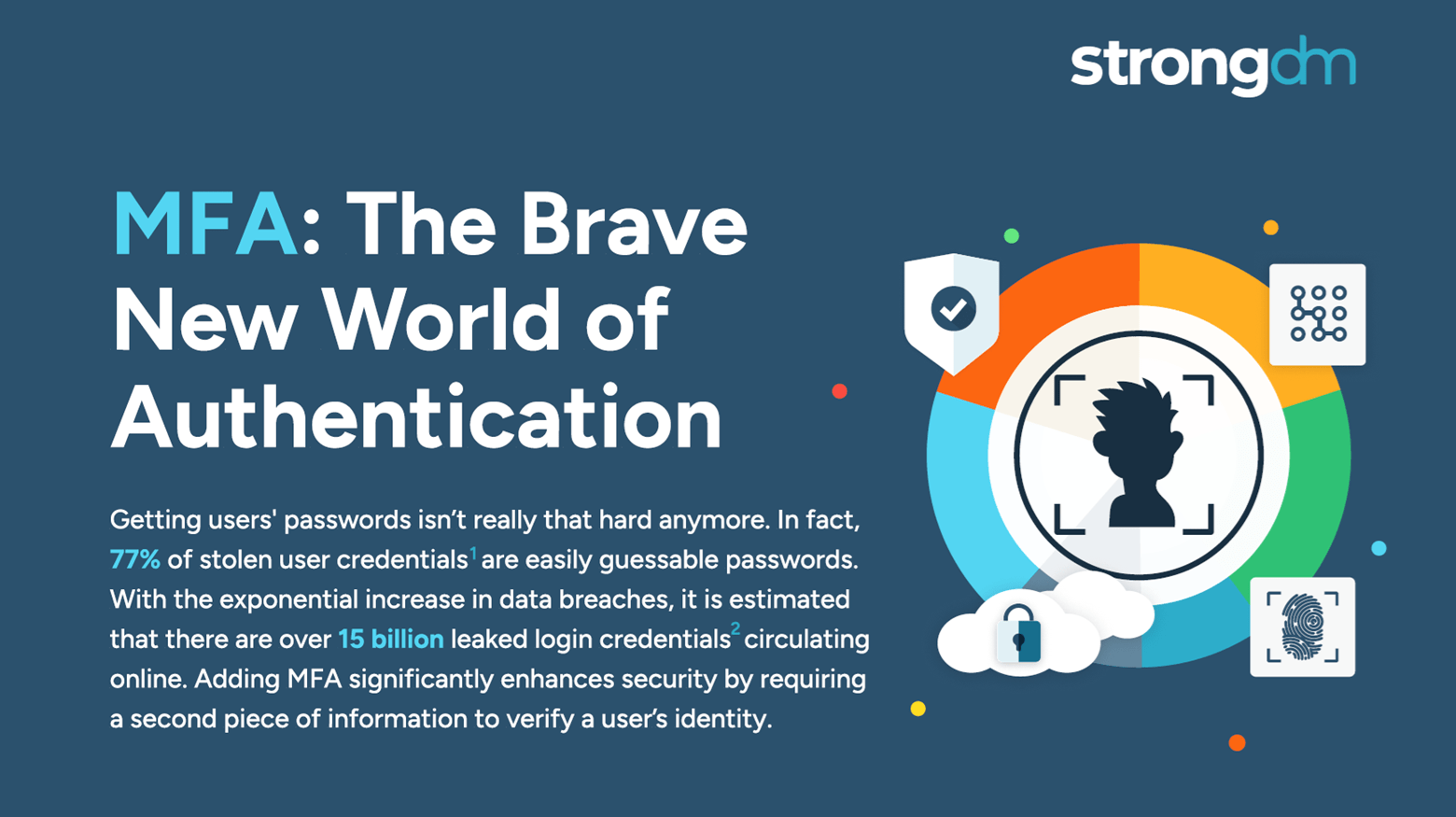
With so many advanced cyber attackers lurking on the threat landscape, a simple password is no longer enough to safeguard your sensitive data. There are many reasons to adopt MFA for your business. It supplements your security by requiring additional information from users upon their access requests—and it significantly reduces your risk of incurring a breach. Several multi-factor authentication methods are available, with varying strengths and weaknesses. Be sure to compare the differences