We’ve just launched our AWS Management Console, adding yet another supported authentication method to improve control and auditability–so you can protect your business and improve employee productivity.
Posts by Category:
- Security
- Access
- DevOps
- Privileged Access Management
- Auditing
- Zero Trust
- Policy
- Compliance
- SOC 2
- Authentication
- Databases
- Identity and Access Management
- Compare
- Team
- Product
- Integrations
- Kubernetes
- AWS
- Engineering
- Productivity
- Podcasts
- Observability
- SSH
- HIPAA
- ISO 27001
- Dynamic Access Management
- Role-Based Access Control
- Secure Access Service Edge
- Webinars
- Events
- NIST
- Onboarding
- Passwordless
- Offsites
- Platform
- PCI

Secured authentication to databases and applications is crucial to enterprise cybersecurity management. Unfortunately, 82% of all breaches involve human error, including misused or compromised credentials that give threat actors unauthorized access to network resources. Luckily, there’s a solution that ensures security without the risks that come with traditional, credential-based authentication. This article discusses token-based authentication and explains why it's a reliable and flexible
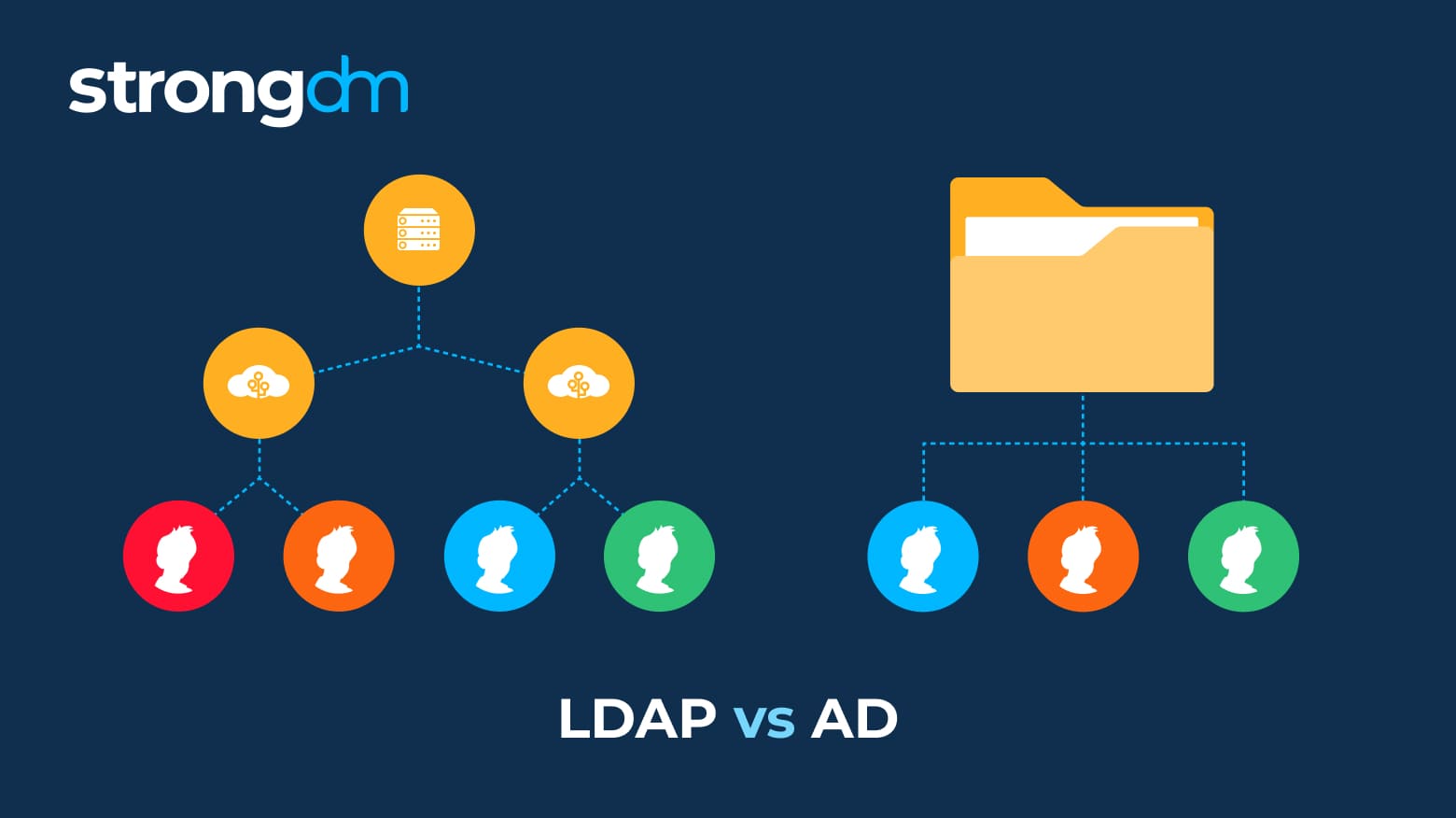
Struggling to understand the difference between Active Directory and LDAP? Don't worry, we’ll make it simple. These are just two among many methods that can provide secure user authentication and authorization. The information in this article will help you decide if LDAP or Active Directory is right for your organization. Robust security and a seamless user experience are attainable, and you can have both!
In this article, we will provide a high-level overview of the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) and Open Authorization (OAuth) information access frameworks. You’ll learn about the key similarities and differences between SAML and OAuth, the unique benefits of each framework, and specific use cases for each. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of SAML and OAuth to help you determine which is right for your organization.
In this article, we’ll define credential stuffing and explain the risks that credential stuffing attacks pose to organizations and customers. We’ll cover recent examples of credential stuffing attacks and discuss how to detect and prevent them. By the end of the article, you should understand the full scope of credential stuffing, including how to protect your customers’ and employees’ account credentials with the right tools.
In this article, we’ll take a comprehensive look at brute force attacks: what they are, how they work, and the different shapes they can take. You'll learn about popular tools utilized by hackers and examples of brute force attacks in action. By the end of this article, you'll be able to understand critical prevention measures for brute force attacks.
The main difference between SAML and OIDC is that SAML builds the trust relationship between the service provider (SP) and the IdP, whereas OIDC trusts the channel (HTTPS) that is used to obtain the security token.
The difference between SAML and LDAP is that SAML is designed for cloud-based connections using only an IdP and SP to communicate user data. LDAP, however, is typically used for accessing on-premises resources by installing a client on the user's device to connect with a directory service.

In this article, we’ll take a look at what authentication vulnerabilities are, how they emerge, and how these issues can affect your organization. Also, you’ll learn about the most common authentication-based vulnerabilities and their implications. By the end of this article, you’ll know the best practices to prevent these authentication issues and keep sensitive data safe.
When it comes to self-hosting critical web infrastructure, modern security requires more than simply siloing an appliance to a local network. In this article, we will discuss new methods for authentication bypass vulnerabilities, simplify end-user experiences, and satisfy compliance requirements—without the need for legacy VPN solutions. Here’s how.

In this article, we will take a deep dive into WebAuthn and some of its associated authentication concepts. We’ll go over the history of WebAuthn and help you better understand the benefits and challenges of using this standard of secure authentication. By the end of this WebAuthn guide, you’ll be able to fully define the concept and grasp how to incorporate it into your organization's security program and web applications.
In this article, we will take a big-picture look at FIDO2 and how it applies to passwordless authentication. You’ll learn about the origins of FIDO2, its advantages and disadvantages, the differences between FIDO2, FIDO, and WebAuthn, and how UAF and U2F differ. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of how FIDO2 works, what problems it solves, whether you need FIDO2 certification, and what that certification entails.
In this article, we dive into passwordless authentication and some of the implications of using this verification method. You’ll learn about examples of passwordless authentication solutions, whether they're secure, and how it's different from multi-factor authentication (MFA). After reading this article, you’ll have a full understanding on how passwordless authentication works and how it can address today’s cybersecurity and access management challenges.